By Sakineh Orangi – Simulation Application Engineer at SolidXperts
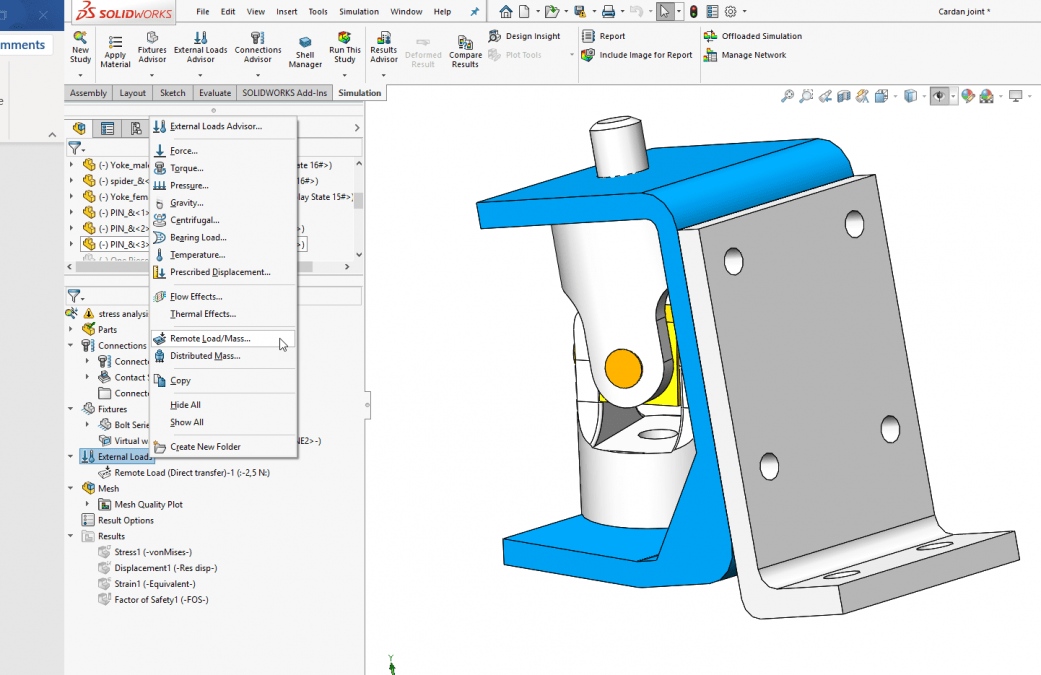
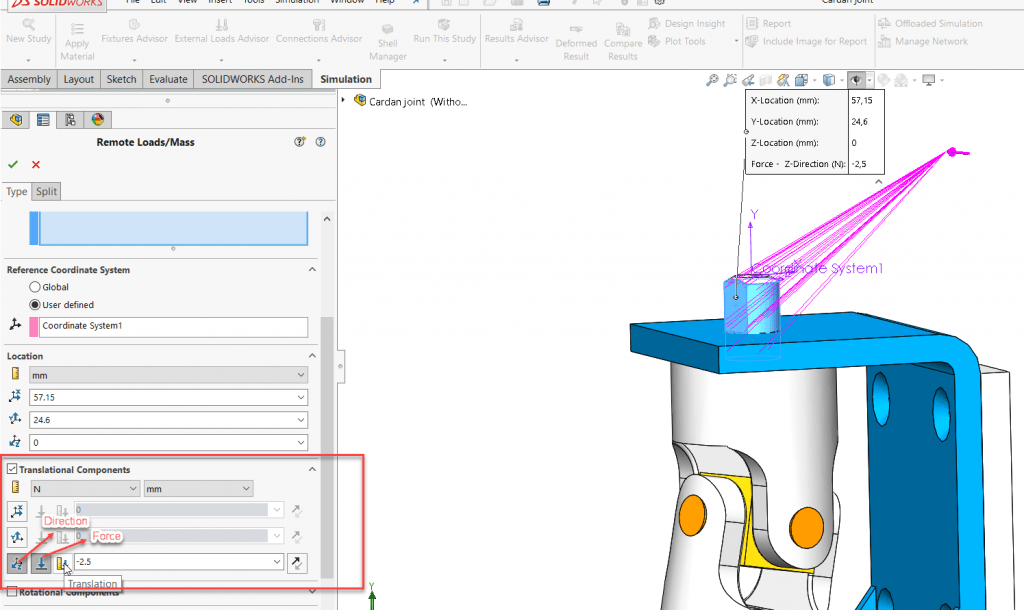
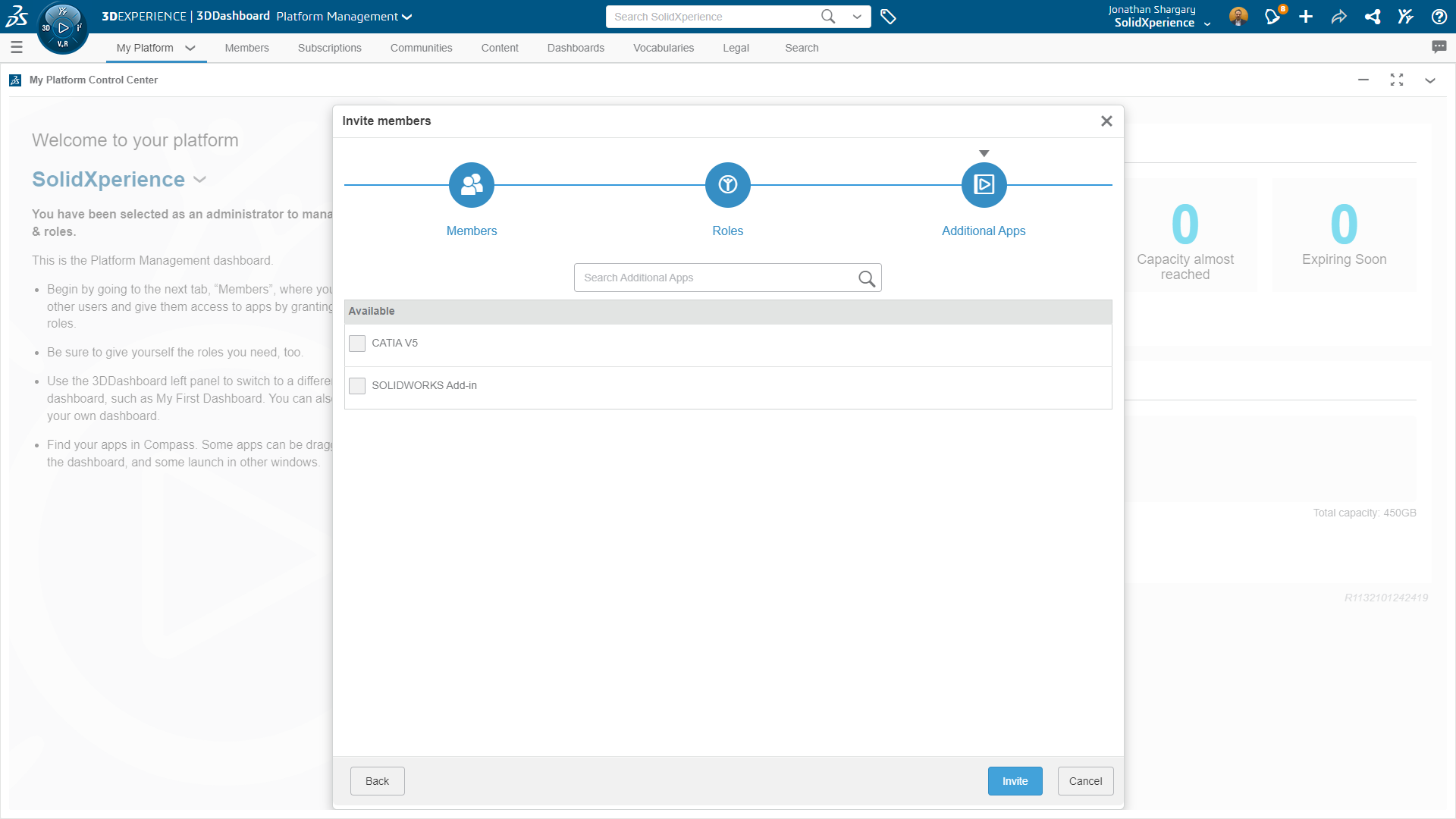
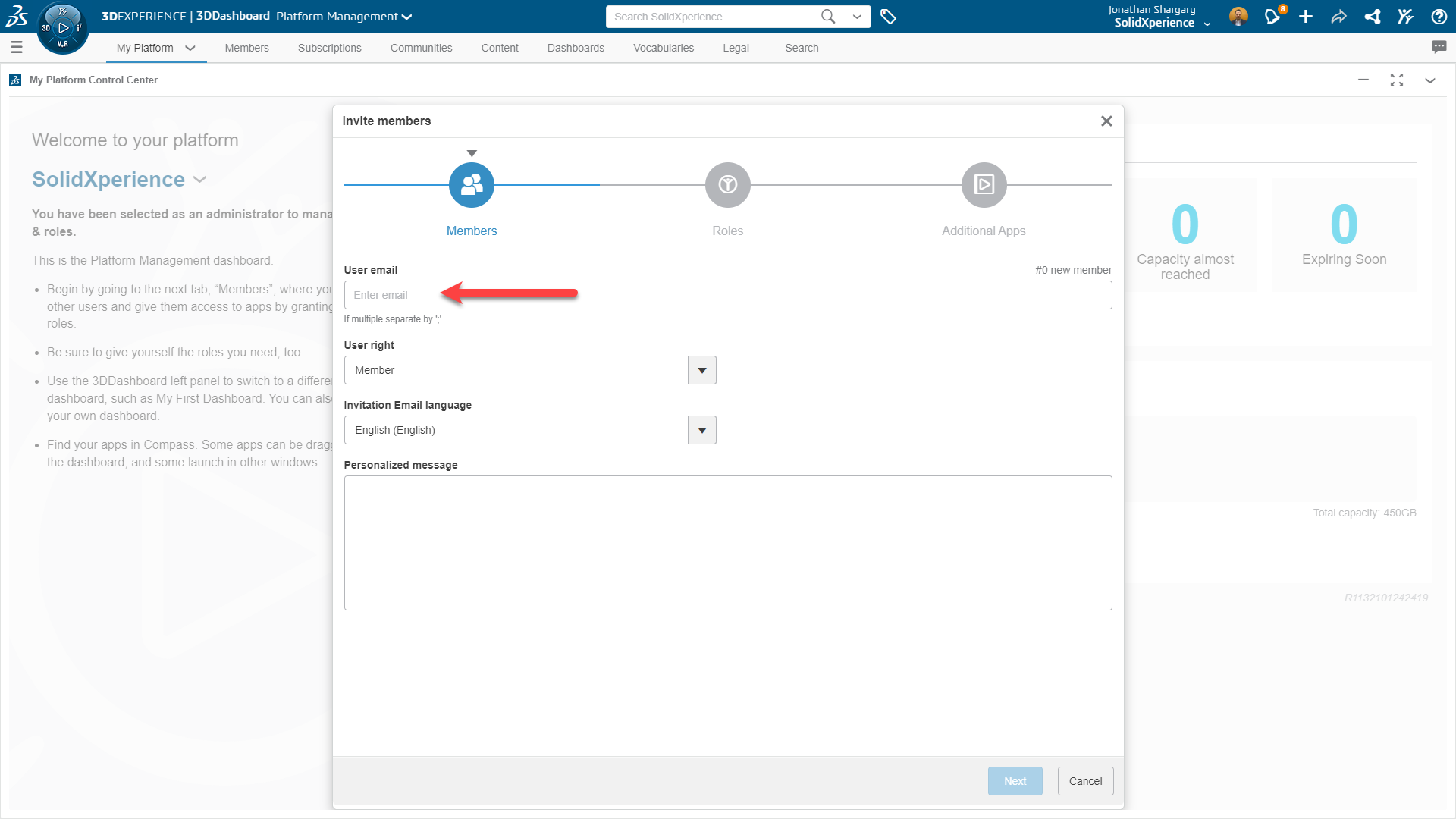
In SOLIDWORKS 2019, the Remote Load/Mass PropertyManager was redesigned to improve the user experience and it introduced distributed coupling. The Remote Loads/Mass PropertyManager allows us to apply remote loads, remote masses, and remote displacements for static, topology, and nonlinear studies. One of the ways to access the Remote Loads/Mass PropertyManager is to right-click on External Loads in the simulation tree of linear static, nonlinear static, or topology.
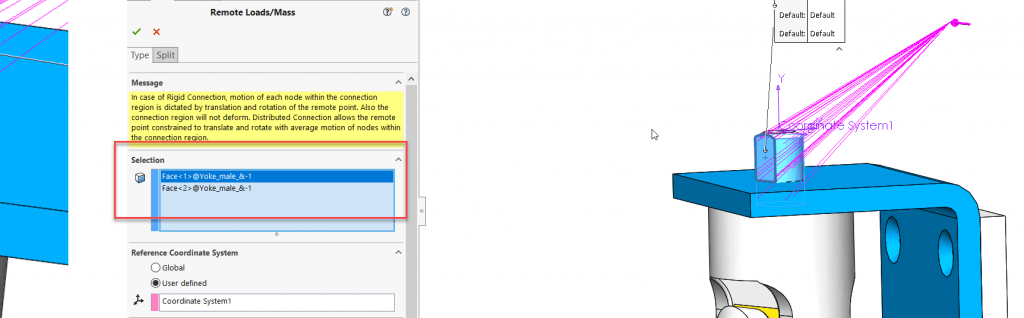
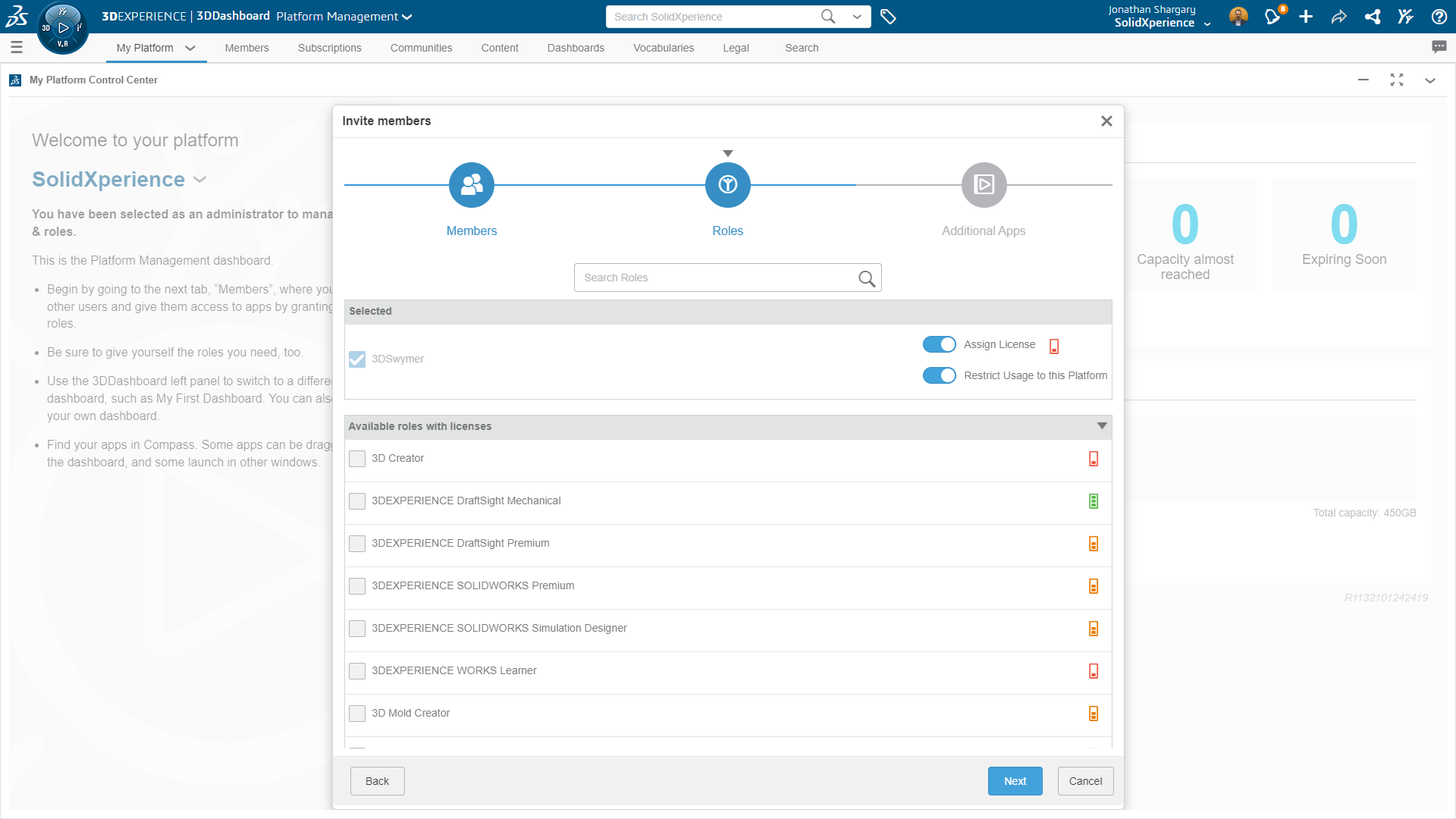
We select the faces to apply remote loads, remote masses, or remote translations and/or rotations.
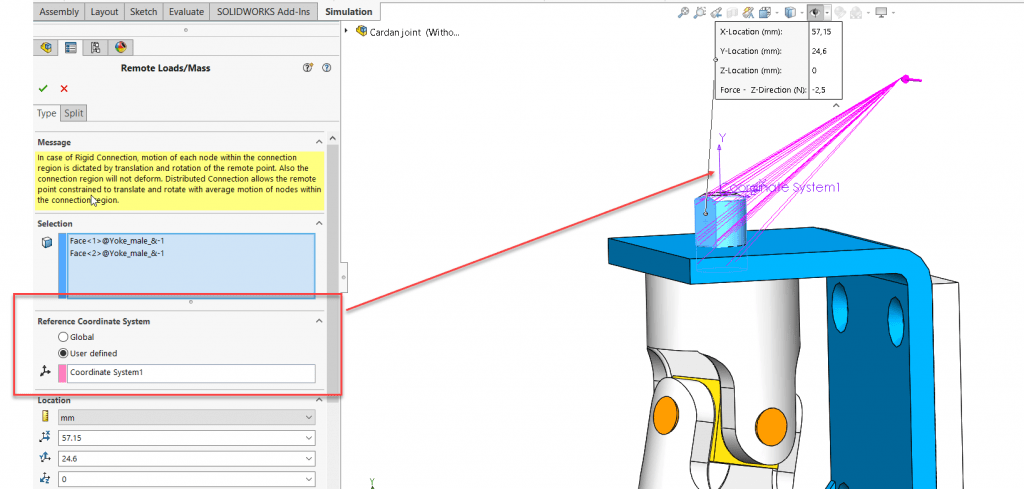
We define the coordinate system used for the interpretation of the location and directions of the remote features.
After this step, we enter the coordinates of the reference node location in a local or global coordinate system.
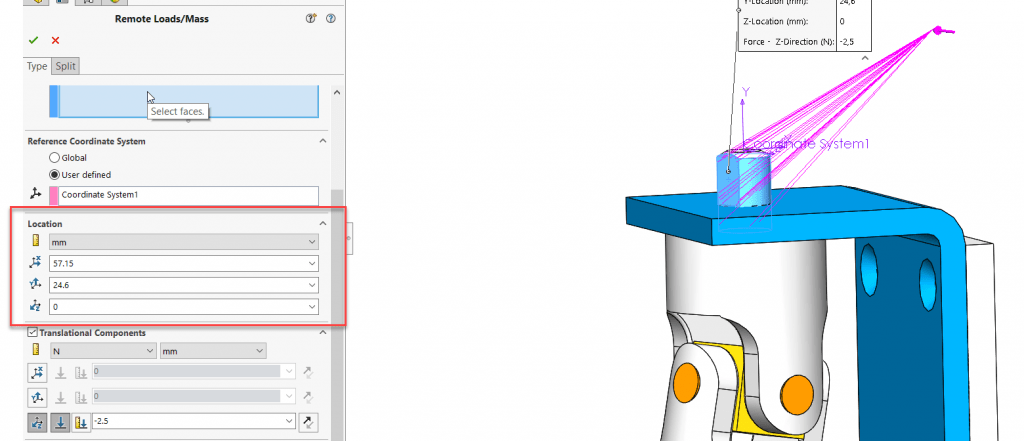
In the case of the definition of remote force or remote distance, we check the Translational Components and enter the values of remote loads or remote translation in the three directions X, Y, and Z.
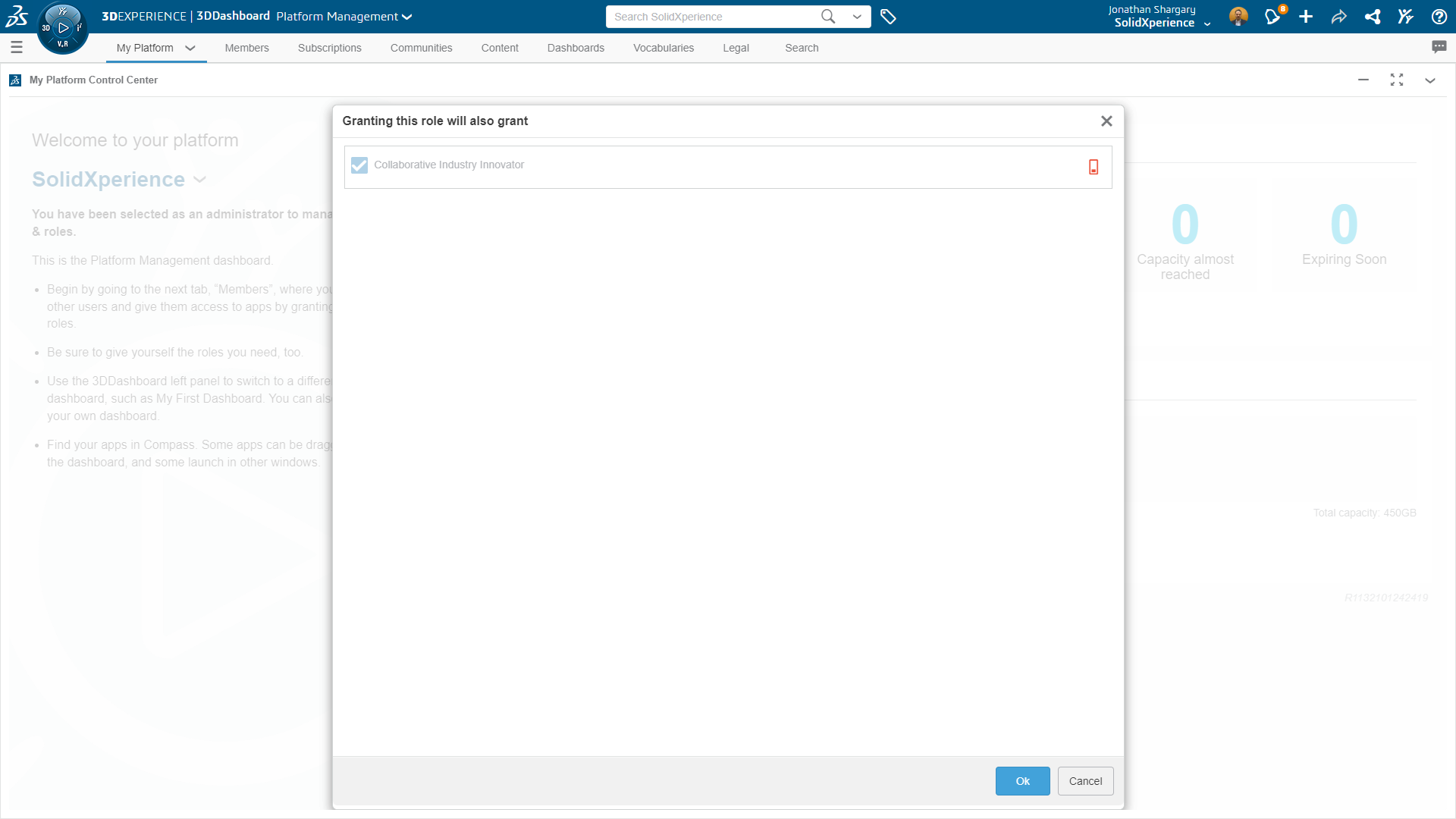
If there are any remote moments or remote rotations, we check Rotational Components and then enter the data.
Learn more about everything new in SOLIDWORKS from 2015 to 2019 by downloading our White Paper.