Designing products in SOLIDWORKS is one of the first steps in an R&D process. However, how can you meet the requirements of various certification bodies? Depending on your field of activity, you may need to comply with standards such as:
- FDA 21 CFR Part 11 (Regulations on electronic records and electronic signatures)
- ISO 9001 (Quality management systems)
- ISO 13485 (Quality management in the medical device industry)
A common requirement among these standards is the availability of an audit trail. SOLIDWORKS PDM already provides a history of your CAD file evolution, but did you know that it also offers tools for generating reliable and increasingly advanced audit trails?
What are the Challenges Related to Audit Trail Production in a PDM System for Certification Compliance?
The following concerns and challenges arise when implementing a Product Data Management (PDM) system while ensuring the presence of audit trails. Taking the previously mentioned standards as examples:
1. Integrity and Security of Audit Trails
To begin with, preventing modification or deletion of logs is essential. Audit trails must be immutable and shielded from unauthorized changes. This is a core requirement of 21 CFR Part 11 and ISO 9001/13485.
Moreover, access control and authentication are critical. Only authorized users should have access, and all actions must be timestamped.
2. Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Traceability of modifications and approvals: Any modification to a document must be recorded with user identity, date, and justification, as per the standards.
PDM system validation: The document management software must be validated to ensure the integrity and reliability of records (21 CFR Part 11).
Archiving and retention of audit trails: Documents and their history must be securely stored and accessible in case of an audit (ISO 13485, FDA).
3. Performance and Data Management
Log volume and performance impact: Continuous activity logging can slow down the system, requiring optimization solutions.
Interoperability with other systems: The PDM must be compatible with other software (ERP, MES, LIMS) while ensuring compliance with regulations.
4. User Training and Awareness
Misuse of functionalities: Lack of training can lead to errors in audit trail recording.
Adapting to regulatory constraints: Compliance processes can be seen as restrictive and may require change management efforts.
In summary, implementing audit trails in a PDM system that complies with FDA 21 CFR Part 11, ISO 9001, and ISO 13485 requires rigorous access management, system validation, data security, and performance optimization. Striking a balance between regulatory compliance and usability is crucial to ensuring effective adoption by teams.
Audit Trails in SOLIDWORKS PDM
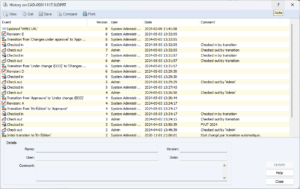
Document History
Each document has a history of its evolution. Recently, SOLIDWORKS PDM has recently added more details regarding document access, particularly check-out operations. Document approval details are also stored in this history and can be considered electronic signatures.
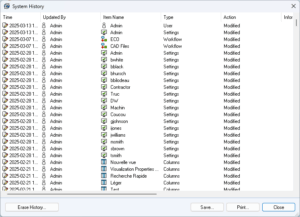
System History in SOLIDWORKS PDM Administration
To ensure the integrity of SOLIDWORKS PDM configurations, a system history log is available. This allows auditors to track system changes, with recorded dates and users responsible for modifications.
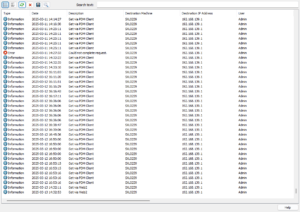
File Access in SOLIDWORKS PDM
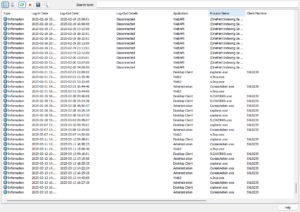
One of the most critical audit trails for security is tracking who accessed specific documents and when. SOLIDWORKS PDM has recently added the capability to log all file access activities, consolidating all operations into a single audit file.
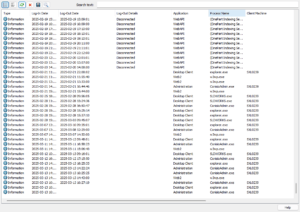
SOLIDWORKS PDM Access Logs
Recently added to SOLIDWORKS PDM audit trails is a log of user login and logout activities. These logs include user connections, workstation details, IP addresses, applications used, and even connections from external systems.
SOLIDWORKS PDM Archive Server Activity Log
SOLIDWORKS PDM compiles archive server activities into a log file. If system errors occur, they are recorded in this log, making it an essential tool for error analysis and troubleshooting.
SOLIDWORKS PDM Client Log File
Each SOLIDWORKS PDM client collects information in a log file, recording communication errors, connections, and disconnections.
Key Takeaway: Audit Trails in SOLIDWORKS PDM as a Pillar of Regulatory Readiness
Audit trail management is a key factor in ensuring compliance with regulatory standards such as FDA 21 CFR Part 11, ISO 9001, and ISO 13485. SOLIDWORKS PDM provides a comprehensive set of tools to ensure data traceability, integrity, and security. With advanced features like document history, access logs, connection tracking, and server/client logs, transparency and regulatory compliance become easier to maintain.
By adopting these tools, companies can enhance quality control, streamline audits, and meet the strict requirements of certification bodies. However, to fully leverage these capabilities, access management must be optimized, systems must be validated, and users must be properly trained. By combining rigor, security, and efficiency, SOLIDWORKS PDM becomes a major asset for compliant and efficient engineering data management.
References
ISO 9001 – Retrieved from: https://www.iso.org/standard/62085.html
FDA 21 CFR Part 11 – Retrieved from: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-11
ISO 13485 – Retrieved from: https://www.iso.org/standard/59752.html